For my diagnostic studies class I will have to look at individual symptoms and the differentials that they are more likely to suggest. So in revers of looking at a pathology I have compiled short lists of non mechanical differentials associated with a presented symptom. I will be expanding on this as I continue my studies so don’t assume that the published article is the final draft!
Dyspnoea:
– Pneumothorax: Trauma, emphysema, cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis (TB).
– Pulmonary oedema: Left sided heart failure.
– Myocardial infarction:
– Pulmonary embolism: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
– Asthma: Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), smoking, infections, anxiety.
– Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) – chronic bronchitis or emphysema.
Clubbed nails:
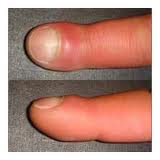
– Congenital cyanotic heart disease: right ventricle under developed.
– Infective endocarditis (IE): Infection of inner heart lining.
– Empyema (pyothorax): pus in the lungs, secondary to lung infection.
– Bronchiectasis: widened bronchi, caused from genetics, obstructions or infections, cystic fibrosis.
– Liver disease – Cirrhosis, alcoholism, viral hepatitis, bile duct obstruction (cholestasis or gallstones), chronic heart failure, autoimmune.
– Ulcerative colitis or Crohns: Congenital, childhood history of antibiotics (prolonged), auto-immune diseases.
Neck pain:
– TB (of the cervical spine): weakens vertebrae.
– Cervical spondylosis: degeneration.
– Cervical disk lesion: Trauma.
– Myocardial infarction (MI): Feeling of impending death.
– Angina: occurs on exertion.
– Thoracic outlet syndrome: neurovascular compression.
Chest pain:
– Angina: Exertion related.
– MI: deathly feeling.
– Pericarditis or IE: inflammation of the heart muscles or lining.
– Rheumatic fever:
– Heart failure: pulmonary oedema, cor pulmonale.
– Lung patholgies: Pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, TB. Dyspnoea, cough.
Leg pain:
– Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Autoimmune, symmetrical joint inflammation.
– Ankylosing spondylitis: Morning stiffness relieved by activity.
– Intermittent claudication: spinal stenosis, oedema, DVT.
– DVT: oedema, visible superficial veins, low grade fever, calcium channel blockers, oestrogen, high dose of opiods, venous hypertension – right side heart failure.
– Gout: swelling, warmth, redness, fever, pain progressively worse, decreased renal excretion.
– Osteoarthritis: bony end feel.
Oedema:
– Cardiac failure: dyspnoea, lethargy, ascites, cough.
– Liver disease: jaundice, viral hepatitis, alcoholism.
– Renal disease: diabetes, proteinuria.
– DVT: unilateral, female, smoker, immobile, obese, surgery within three months prior, oestrogen therapy, contraceptives.
– Lymphatic flow obstruction: allergens, drug use.
– Trauma/local infection: heat, redness.
Related articles
- How To Avoid Clots In The Leg Veins (DVT) When Traveling (healthhype.com)
- Sweet’s syndrome: a very rare association with pulmonary tuberculosis (sweetssyndrome.wordpress.com)
- Do You Know the 9 Symptoms That Should Never Be Ignored? (rockingchairordancingshoes.wordpress.com)